Hydropower: Harnessing South Africa's Rivers
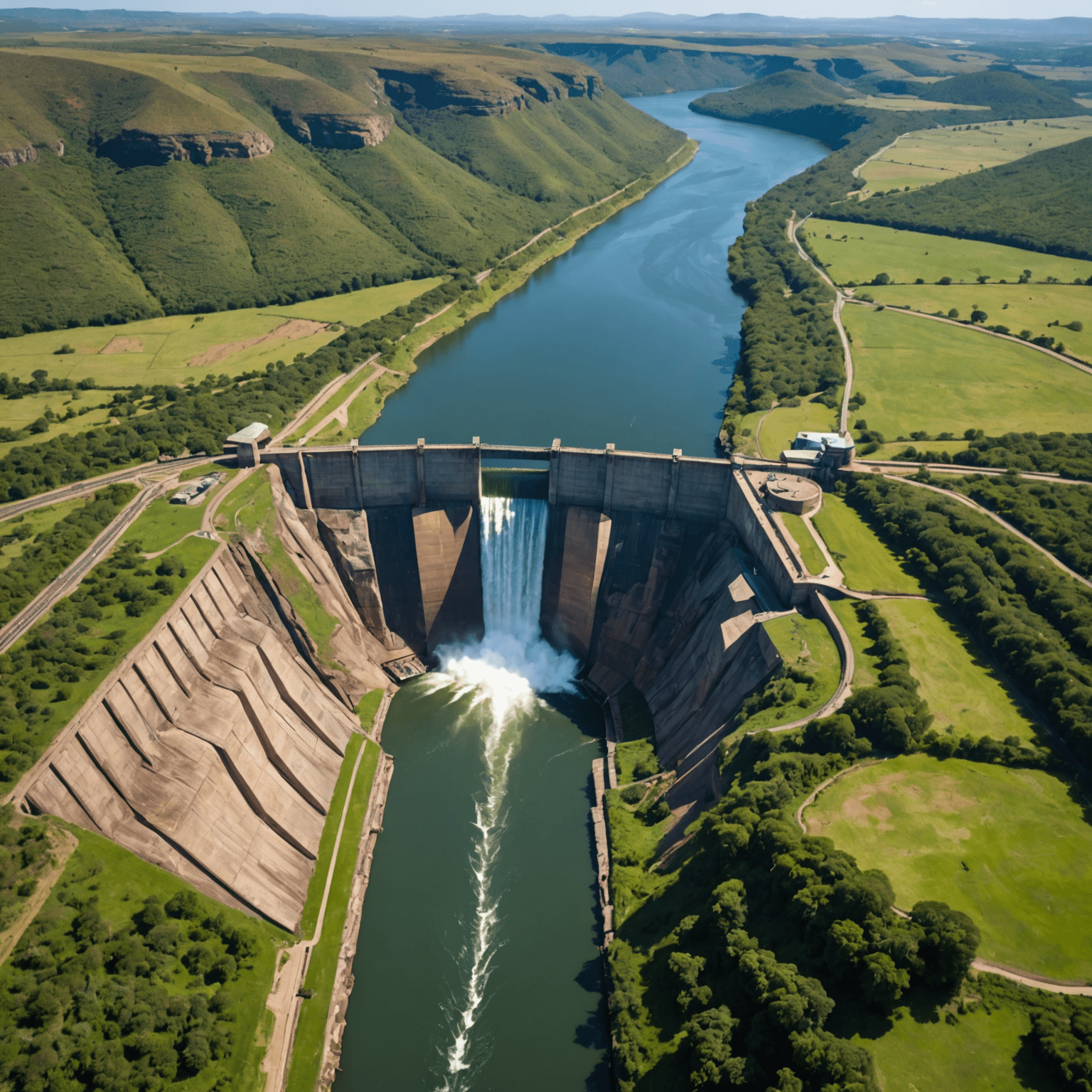
South Africa, with its diverse landscape and numerous rivers, has significant potential for hydroelectric power generation. This renewable energy source could play a crucial role in the country's energy mix, offering both environmental and economic benefits.
Current State of Hydropower in South Africa
While South Africa's electricity generation is predominantly coal-based, hydropower currently contributes a small but important portion to the national grid. The country has several operational hydroelectric facilities, including:
- Gariep Dam (360 MW capacity)
- Vanderkloof Dam (240 MW capacity)
- Drakensberg Pumped Storage Scheme (1000 MW capacity)
- Palmiet Pumped Storage Scheme (400 MW capacity)
These facilities, while significant, represent only a fraction of South Africa's hydroelectric potential.
Small-Scale Hydropower Projects
In recent years, there has been growing interest in small-scale hydropower projects. These installations, typically generating less than 10 MW, offer several advantages:
- Lower environmental impact
- Shorter construction times
- Ability to provide power to remote communities
- Potential for private sector involvement

The Department of Energy has identified numerous potential sites for small-scale hydropower development across the country, particularly in the Eastern Cape, KwaZulu-Natal, and Mpumalanga provinces.
Future Prospects and Challenges
The future of hydropower in South Africa looks promising, with several large-scale projects in various stages of planning and development. These include:
- The proposed Mzimvubu Water Project in the Eastern Cape
- Potential expansion of existing facilities
- Cross-border projects with neighboring countries
However, the development of hydropower in South Africa faces several challenges:
- High initial capital costs
- Environmental concerns, particularly regarding water scarcity
- Regulatory hurdles and lengthy approval processes
- Competition from other renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind
Conclusion
Hydropower presents a significant opportunity for South Africa to diversify its energy mix and reduce its carbon footprint. While challenges exist, the potential benefits in terms of energy security, job creation, and sustainable development make it an attractive option for the country's energy future.
As South Africa continues to develop its renewable energy sector, hydropower is likely to play an increasingly important role, complementing other clean energy sources and contributing to a more sustainable and resilient power grid.